How
to Register Your Own Domain Name on Godaddy.Com
One of the many
reasons the Internet is so powerful is because it gives nearly anyone the
ability to contribute their voice and knowledge to the rest of the world. A
particularly popular way to make yourself known is to set up a website.
These days many
services, such as Google Pages or WordPress, offer websites on commercial
domains, but in a lot of cases it makes more sense to have your website on your
own domain--a personal place on the Internet where you are in complete control
of what is published and how it looks. Here's how to register your own domain
name.
When setting up your
personal domain name, you have a lot of options and many vendors to choose
from. You can search around to see what works best for you and your needs, but
the following steps outline the gist of what you need to do:
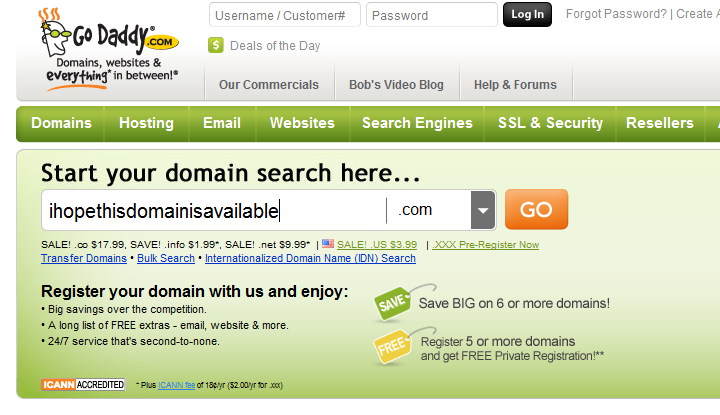
1. Confirm that the name
you want is available. You can begin your search at a name registrar such as GoDaddy. Be
creative, as your domain will be the central focus of your entire site. If
you're looking to reserve a domain name, start at a domain name registrar such
as GoDaddy.

2. If the name is
available, you will have the choice to register the domain on several different
top-level domains if available, such as .org, .biz, and .net. If the name is
not available, simply try again. Hundreds of millions of domains are already
registered, so this step can be difficult. Don’t give up!
3. After selecting the
top-level domains you wish to register with, the last choice to make is for how
long you want to reserve the name. You can buy domain names in year-long
increments, up to a maximum of ten years.
You might be able to save some cash
by picking a slightly different domain name.
4. When you have
finalized the name, the top-level domains it should be on, and the amount of
time you want to hold the rights to the name, you need to pay the registrar to
make the registration for you. Once you pay, you own the domain name.
Now that your domain
is registered, all you need to do is specify where computers looking for your
domain should go (namely, the IP address where your domain’s website is hosted)
by updating your site's nameservers. If you do not have a place to host your website or
information, most registrars have hosting as an available option during the
registration process. Taking this option is the easiest path, because you don't
need to worry about any additional setup.


